22 Primary Care
22.1 Developmental Milestones
| Gross Motor | Fine Motor | Social Language/Self-Help | Verbal Language | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Visit | Reflexively moves arms and legs, Lifts head briefly when on stomach | Keeps hands in fists | Periods of wakefulness, Looks at parent when awake, Calms when picked up | Cries with discomfort, Calms to parent’s voice |
| 2m | Lifts head and chest when on stomach, Keeps head steady when sitting | Opens and shuts hands, Briefly brings hands together | Smiles responsively, Makes sounds to show happiness/upset | Makes cooing sounds |
| 4m | Supports self on elbows and wrists when on stomach, Rolls from stomach to back, Pushes down on legs when feet on hard surface | Keeps hands unfisted, Plays with fingers in midline, Grasps objects | Laughs, Looks for caregiver when upset | Turns to voices, Makes extended cooing sounds, Begins to babble |
| 6m | Rolls from back to stomach, Sits briefly without support, Supports weight on legs while held “standing” | Passes toys between hands, Rakes small objects, Bangs small objects on surfaces | Pats or smiles at own reflection, Looks when name is called, Knows familiar faces | Babble, “ga,” “ma,” “ba,” Responds to sounds by making sounds |
| 9m | Sits well without support, Pulls to stand, Crawls | Picks up food to eat, Picks up small objects with 3 fingers and thumb, Lets go of objects intentionally, Bangs objects together | Uses basic gestures (wave bye), Looks for dropped objects, Turns when name is called, Plays Peek-a-boo, May be afraid of strangers | Says “Dada” “Mama” nonspecifically, Copies sound that parent makes, Looks around when hearing things like “where’s your bottle?” |
| 12m | Cruising, May take first independent steps, Stands without support | Uses 2-finger pincer grip, Picks up food to eat, Drops objects in a cup, Uses index finger to point | Looks for hidden objects, Imitates new gestures, May be shy or nervous with strangers, Cries when parents leave | Uses “Dada” “Mama” specifically, Uses 1 other word, Makes sounds with changes in tone, Follows directions with gestures |
| 15m | Squats to pick up objects, Crawls up a few steps, Runs | Makes marks with crayon, Drops objects in and takes objects out of container | Imitates scribbling, Points to ask for something | Uses 3 words other than names, Follows directions without a gesture |
| 18m | Walks up steps with 2 feet per step, Sits in small chair, Carries toy while walking | Scribbles spontaneously, Drinks from a cup, Eats with a spoon | Engages with others for play, Helps dress and undress self, Points to pictures in book, Uses words to ask for help | Identifies at least 2 body parts, Names at least 5 familiar objects |
| 2y | Jumps on 2 feet, Kicks a ball, Begins to run, Walks up and down stairs holding on | Stacks objects, Turns book pages, Draws lines and circles, Uses hands to turn objects (i.e. door) | Plays alongside other kids, Takes off some clothing, Shows defiant behavior and more independence, Copies others | Uses 50 words, combines two to four words in short phrases, 50% understandable speech, Follows 2-step command, Names 5 body parts, Repeats words overheard in conversation (careful!) |
| 3y | Pedals a tricycle, Jumps forward, Climbs on and off chair/couch, Runs well | Draws a circle, Draws a person with head and 1 body part, Cuts with child scissors | Puts on coat, jacket by themselves, Eats independently, Enters bathroom and urinates independently, Imaginative play, shares | 3 word sentences, 75% of words are understandable to strangers, Tells a story from a book, Understands simple prepositions, Carries on conversation with 2-3 sentences |
| 4y | Skips on 1 foot, Climbs stairs, alternating feet without support | Draws simple cross, Draws person with 3 body parts, Unbuttons/buttons, Grasps pencil with thumb and fingers | Enters bathroom and has bowel movement independently, Brushes teeth, Dresses and undresses self, Well-developed imaginative play, Cooperates with others | Tells stories, words 100% intelligible to strangers, Follows simple rules in game, Draws recognizable pictures |
| 5y/6y | Balances on 1 foot, hops, skips | Can draw person with 6 body parts, Copies squares and triangles, Prints some letters/numbers, Can tie a knot | Follows simple directions, Dresses with minimal assistance, Aware of gender, Wants to please friends, wants to be like friends | Counts to 10, Names 4 or more colors, Speaks very clearly, Tells a simple story using full sentences |
Milestones from Bright Futures and CDC
Early Intervention is responsible for assessing developmental delays and providing appropriate support in children birth through 2 years and 9 months. The Public School System is responsible for assessing deficits and providing appropriate support after 2.9 years. Their initial assessment is called a “TEAM evaluation.” An Individualized Education Plan (IEP) is developed after the TEAM evaluation.
22.2 Red Flags
REGRESSION (loss of skills) & PARENTAL CONCERN are red flags at any age
Asymmetry
Idiosyncratic speech, disordered sequence of development
Poor intelligibility for age
Abnormal tone or movement patterns at any age, spasticity, hypotonia, absent DTRs
Persistent primitive reflexes
Lack of developmentally appropriate response to visual stimuli
Immature play (like younger child)
Stereotypic play; lack of pretend
School failure (either for specific subjects like reading or math, or generalized)
Always check vision and hearing if any concerns – can be assessed as young as newborn
Emotional dysregulation
Abnormal attachment patterns (over-clingy, indiscriminate)
Using one hand exclusively at any age
Problems w/ feeding and/or swallowing
Age-Specific:
Poor head control at 5 mos
Limited social smiling and shared enjoyment by 6 mos
Parent suspects hearing loss, babbling stops at >6 mos, lack of response to sound (check hearing!)
Lack of transfer at 7 mos
Not sitting independently w/ hands-free at 8 mos
Not rolling back-front, not taking weight well through the legs when held at 9 mos
Limited gestures like pointing response to name, joint attention by 12 mos
No single words by 15 mos
Not walking by 18 mos
Limited social imitative play by 18 mos (e.g. imitating housework)
No combos by 24 mos
Limited pretend play (e.g. feeding doll) by 24 mos
Stutter past 3 ½ yrs (or earlier if anxiety/mannerisms)
Delayed self care (ADLs) at 4 yrs
Delayed printing at school entry
No friends at school age
22.3 Newborn Visit
22.3.1 HPI
22.3.1.1 BIRTH/PREGNANCY HISTORY
G/Ps, prenatal labs
Gestational age, birth method, GBS status, whether sepsis r/o required at birth
22.3.1.2 IN/OUTs
Feeding (8-12/24 hrs): breastfed vs. formula vs. mixed- go over feeding cues (rooting, hands to mouth, fussing)
No more than around 4 hours w/o feeding.
Stool: transitioning from meconium (black, sticky) -> green -> yellow and seedy
Urine: multiple times per day (# of voids = days of life up until DOL 6, then >6/day)
22.3.1.3 SLEEP
Supine, in own separate space on flat, firm mattress w/o pillows, blankets, or stuffed animals.
Discuss dangers of co-sleeping
Room sharing recommended for first 6 months
Discuss harm reduction (no alcohol/smoking, consider bringing bassinet into bed) if family is going to cosleep
22.3.1.4 DEVELOPMENT
See chart above
22.3.2 Exam
Full exam including red reflex, Ortolani and Barlow maneuvers, umbilical exam
Weight check: % of birth weight (should regain BW by 10-14 days)
Check for dysmorphic features
22.3.3 A/P
22.3.3.1 Immunizations/Supplements
Has child received Hep B in nursery? If no, give today.
Vitamin D (400 IU daily) if exclusively breastfeeding or taking <32 oz of formula.
22.3.3.2 Anticipatory Guidance
When to call: jaundice, temperature >100.4F, decreased feeding, decreased urine
Development: Impossible to spoil an infant, intermittent tummy time when supervised
Sleep: Safe sleep as above
Nutrition:
- If formula fed, go over how to properly mix formula, should take about 3-4 oz every 3-4 hours
- If breastfeeding, go over safe storage of breastmilk
- Breastmilk rule of 4’s - can be left at room temperature (77 F or colder) for 4 hours, refrigerator (40 F) for 4 days or freezer (<0F) for up to 6 months (best) to 12 months (acceptable)
Safety: Rear facing car seat, avoid smoke, avoid hot liquids while holding baby, umbilical stump care
Caregiver: Normalize caregiver feelings, offer community supports, can introduce idea of planning ahead re day care but may be too early and overwhelming at this stage for some families
22.3.3.3 Follow Up
Determine if infant needs weight check
1 month visit
22.4 2 Month WCC
22.4.1 HPI
22.4.1.1 IN/OUTs
Feeding (8-12/24 hrs): breastfed vs. formula vs. mixed
Stool: yellow and seedy
Urine: multiple times per day
22.4.1.2 SLEEP
Supine, in crib w/o pillows, blankets, or stuffed animals.
Discuss co-sleeping
22.4.1.3 DEVELOPMENT
See chart above
22.4.2 Exam
Full exam including red reflex, Ortolani and Barlow maneuvers Weight, length, height: head circumference, growing along curve
22.4.3 A/P
22.4.3.1 Immunizations/Supplements
Vaccines: Hep B #2, Hib #1, DTaP #1, IPV #1 , PCV #1, Rotavirus #1 (NOTE: CHPCC gives HepB # 2 @ 1 month)
Vitamin D (400 IU daily) if exclusively breastfeeding (should start at newborn visit)
22.4.3.2 Anticipatory Guidance
When to call: Temperature, decreased feeding, decreased wakefulness
Development: Risk of falling once learn to roll, unswaddle arms at night once rolling, develop a plan for fussy periods
Sleep: safe sleep, place in crib before fully asleep
Nutrition: If formula feeding, should take about 3-6 oz 5-8 times per day, wait to introduce solids until 4-6 months, no water or cow’s milk
Safety: Rear facing car seat, avoid smoke, hand on baby at all times while on high surfaces
Caregiver: Go over caregiver supports, family planning, daycare options
Dental: Avoid putting to bed w/ bottle
22.4.3.3 Follow Up
4 month CPE
22.5 4 Month WCC
22.5.1 HPI
22.5.1.1 IN/OUTs
Feeding Q4-5 hours. breastfed vs. formula vs. mixed
Assess if started any purees/table foods
Stool: yellow and seedy
Urine: multiple times per day
Assess family history of severe food allergy/eczema
22.5.1.2 SLEEP
Supine, in crib w/o pillows, blankets, or stuffed animals
22.5.1.3 DEVELOPMENT
See chart above
22.5.2 Exam
Full exam including red reflex, Ortolani and Barlow maneuvers
Weight, length, height: head circumference, growing along curve
22.5.3 A/P
22.5.3.1 Vaccines/Supplements
Vaccines: Hib #2, DTaP #2, IPV #2, PCV #2, Rotavirus #2
Poly-Vi-Sol + IRON if > 50% breastfed or taking <32 oz formula per day
22.5.3.2 Anticipatory Guidance
When to call: Temperature, decreased feeding, decreased wakefulness
Development: Provide safe opportunities to explore, continue tummy time, calming strategies for fussy periods, unswaddle arms at night once rolling, begin to learn baby’s temperament
Sleep: Place in crib before completely asleep, back to sleep, decrease overnight feeds
Nutrition: If formula feeding should take about 4-6 oz 4-6 times per day, introduce solids (1 at a time), introduce peanut (peanut butter in baby oatmeal is good option), discuss dietary sources of iron (iron fortified cereal, pureed meat, dark leafy greens), discuss choking hazards
Safety: Start baby proofing, keep small objects away from baby, keep one hand on baby, rear facing car seat
Caregiver: Go over caregiver supports, family planning, daycare options
Dental: Avoid putting to bed with bottle
22.5.3.3 Follow Up
6 month CPE
22.6 6 Month WCC
22.6.1 HPI
22.6.1.1 IN/OUTs
Feeding Q4-5 Hours, breastfed vs. formula vs. mixed
Ask if started solids (if so, stool might be less frequent, firm/hard, constipation)
Stool: yellow and seedy
Urine: multiple times per day
22.6.1.2 SLEEP
Supine, in crib w/o pillows, blankets, or stuffed animals
22.6.1.3 DEVELOPMENT
See chart above
22.6.2 Exam
Full exam including red reflex, Ortolani and Barlow maneuvers
Teeth?
Weight, length, height: growing along curve
22.6.3 A/P
22.6.3.1 Vaccines/Supplements
Vaccines: Hep B #3, Hib #3, DTaP #3, IPV #3 , PCV #3, Rotavirus #3 Eligible for flu vaccine (need two to complete series, separated by 1 month)
Continue Poly-Vi-Sol + IRON if > 50% breastfed or taking <32 oz formula per day
22.6.3.2 Anticipatory Guidance
When to call: Temperature, decreased feeding, decreased wakefulness
Development: Engage in reciprocal play, read to baby
Sleep: Safe sleep, put baby to sleep awake but drowsy, try to eliminate night time feeds
Nutrition: If formula feeding, should take about 6-8 oz 3-5 times per day, continue to work on solid food introduction (1 at a time), ensure baby has had peanut, go over dietary sources of iron (iron fortified cereal, pureed meat, dark leafy greens), discuss choking hazards, delay cow’s milk until1 year old, okay to offer small amounts of water
Safety: Baby proof home, keep small objects away, give poison control number (1-800-222-1222), rear facing car seat, avoid baby walkers, don’t leave baby alone in the tub
Caregiver: Use trusted child care providers
Dental: Brushing/wiping down teeth to build habits
22.6.3.3 Follow Up
9 month CPE
22.7 9 Month WCC
22.7.1 HPI
22.7.1.1 IN/OUTs
Feeding Q4-5 hours. breastfed vs. formula vs. mixed
Solids, no overnight feeds
Stool: might be less frequent since starting solids, ask if stool if firm/hard and if pt having abdominal distention (these are signs of constipation)
Urine: multiple times per day
22.7.1.2 DEVELOPMENT
See chart above
22.7.2 Exam
Full exam
Weight, length, height: growing along curve (head circum)
22.7.3 A/P
22.7.3.1 Vaccines/Supplements/Screenings
Vaccines: check that have received 3 of: Hep B, Hib, DTaP, IPV, PCV, Rotavirus
Eligible for flu vaccine (needs 2 to complete series)
CBC and lead screening
Continue Poly-Vi-Sol + IRON if > 50% breastfed or taking <32 oz formula per day
22.7.3.2 Anticipatory Guidance
When to call: Temperature, decreased feeding, decreased wakefulness
Development: Develop daily routine, allow for safe exploration, discuss separation anxiety, read/talk/sing together, avoid screens if possible, focus on positive reinforcement/redirection for discipline, start to learn baby’s temperament
Sleep: Eliminate overnight feeds, develop bedtime routine
Nutrition: If formula feeding should take about 7-8 oz 3-4 times per day, increase table food to 3 meals and 2-3 snacks, start to introduce more textures, avoid juice, avoid cow’s milk until 1, encourage starting to wean from bottle to cup, discuss choking hazards
Safety: Rear facing car seat until age 2 or highest weight allowed by manufacturer , keep small objects away, avoid baby walkers, poison control number (1-800-222-1222), be within arm’s reach near water/pools/bathtubs
Dental: Brush teeth, avoid bottle in bed
22.7.3.3 Follow Up
12 month CPE , 1st dental visit at 1 year old or w/i 6 months of 1st tooth eruption
22.8 12 Month WCC
22.8.1 HPI
22.8.1.1 IN/OUTs
Goals to have social meals, eat w/ family if feasible, 3 meals and 2-3 snacks spaced evenly.
Transition from formula to whole milk
Solids, no overnight feeds
Stool: might be less frequent since starting solids, ask if stool if firm/hard and if pt having abdominal distention (these are signs of constipation)
Urine: multiple times per day
22.8.1.2 DEVELOPMENT
See chart above
22.8.2 Exam
Full exam - ensure testes are descended bilaterally
Weight, length, height: growing along curve (head circum)
22.8.3 A/P
22.8.3.1 Vaccines/Supplements/Screenings
Vaccines: PCV#4, MMR#1, VZV#1
Eligible for flu vaccine (needs 2 to complete series)
CBC/lead screening if not done at 9 months
Ensure ferrous sulfate started if evidence of iron deficiency anemia
22.8.3.2 Anticipatory Guidance
When to call: Temperature, decreased feeding, decreased wakefulness
Development: Develop daily routine, focus on positive reinforcement/redirection for discipline, limit screen time, read/sing/talk together, options for developmentally appropriate play
Sleep: Continue 1 nap a day, nightly bedtime routine, try to introduce a comfort object (blanket, stuffed animal) to help with any nighttime awakenings
Nutrition: Should be transitioned to cow’s milk (limit 16-24 oz per day), transition to cup from bottle, 3 meals with 2-3 snacks per day, trust a toddler to know how much to eat, continue to introduce textures, discuss choking hazards
Safety: Rear facing car seat until age 2 or highest weight allowed by manufacturer , childproof home, poison control number (1-800-222-1222), be within arm’s reach near water/pools/bathtubs, discuss gun safety
Dental: Make first dental appointment, brush teeth twice a day with plain water, no bottle in bed
22.8.3.3 Follow Up
15 month CPE, 1st dental visit at 1 year old or w/i 6 months of 1st tooth eruption
22.9 15 Month WCC
22.9.1 HPI
22.9.1.1 IN/OUTs
Eat w/ family, 3 meals and 2-3 snacks spaced evenly.
Drinks whole milk
Solids, no overnight feeds
Stool: might be less frequent since starting solids, ask if stool if firm/hard and if pt having abdominal distention (these are signs of constipation)
Urine: multiple times per day
22.9.1.2 DEVELOPMENT
See chart above
22.9.2 Exam
Full exam including red reflexes and dental exam
Weight, length, height: growing along curve (head circum)
22.9.3 A/P
22.9.3.1 Vaccines
HepA#1, DTap#4, Hib#4, flu if hasn’t had
22.9.3.2 Anticipatory Guidance
When to call: Temperature, decreased feeding, decreased wakefulness
Development: Try to allow child to choose between 2 options, stranger anxiety is normal at this age, read/sing/talk together, focus on positive reinforcement/redirection for discipline, limit screen time
Sleep: Maintain consistent bedtime routine, try to introduce a comfort object (blanket, stuffed animal) to help with any nighttime awakenings, should still take 1 daily nap
Nutrition: Should be transitioned to cow’s milk (limit 16-24 oz per day), fully transition to cups from bottles, 3 meals with 2-3 snacks per day, trust a toddler to know how much to eat, continue to introduce textures, discuss choking hazards
Safety: Rear facing car seat until age 2 or highest weight allowed by manufacturer , childproof home, poison control number (1-800-222-1222), be within arm’s reach near water/pools/bathtubs, discuss gun safety
Dental: Ensure they have had first dental visit, twice daily brushing, no bottle in bed
22.9.3.3 Follow up
18 month CPE, 1st dental visit at 1 year old or w/i 6 months of 1st tooth eruption
22.10 18 Month WCC
22.10.1 HPI
22.10.1.1 IN/OUTs
Eat w/ family, 3 meals and 2-3 snacks spaced evenly. Drinks whole milk
Starts developing preferences, important to introduce healthy foods multiple times
Stool: might be less frequent since starting solids, ask if stool if firm/hard and if pt having abdominal distention (these are signs of constipation)
Urine: multiple times per day
22.10.1.2 DEVELOPMENT
See chart above
22.10.2 Exam
Full exam including red reflexes and dental exam
Weight, length, height: growing along curve (head circum)
22.10.3 A/P
22.10.3.1 Vaccines/Screenings
Vaccines: Catch-up and flu
MCHAT for Autism
22.10.3.2 Anticipatory Guidance
When to call: Temperature, decreased feeding, decreased wakefulness
Development: Reinforce limits and appropriate behavior, focus on positive praise, allow child to choose between 2 options when possible, limit screen time, talk/read frequently with your child in simple words to help with language
Sleep: Maintain consistent bedtime routine, try to introduce a comfort object (blanket, stuffed animal) to help with any nighttime awakenings, should still take 1 daily nap
Nutrition: Ensure no more than 16-24 oz cow’s milk daily, ensure no more bottle, trust a toddler to know when they are full, try to have family meal times, often have to offer a new food several times
Safety: Rear facing car seat until age 2 or highest weight allowed by manufacturer , childproof home, poison control number (1-800-222-1222), be within arm’s reach near water/pools/bathtubs, discuss gun safety, install stair/window gates now that child is walking/climbing
Dental: Ensure they have had first dental visit, twice daily brushing, no bottle in bed
22.10.3.3 Follow up
2 year CPE, 1st dental visit at 1 year old or w/i 6 months of 1st tooth eruption
22.11 2 Year Old WCC
22.11.1 HPI
22.11.1.1 IN/OUTs
Eat w/ family, 3 meals and 2-3 snacks spaced evenly. Transition to 1-2% milk.
Starts developing preferences, important to introduce healthy foods multiple times
Beginning of awareness of urges to urinate and stool, discomfort in diaper, interested in toileting
22.11.1.2 DEVELOPMENT
See chart above
22.11.2 Exam
Full exam
Weight, height: growing along curve (head circum)
Observe coordination, language (expressive and receptive), socialization
22.11.3 A/P
22.11.3.1 Vaccines/Screenings
Vaccines: HepA#2 and flu
CBC and lead
MCHAT for autism screening
22.11.3.2 Anticipatory Guidance
When to call: Temperature, decreased feeding, decreased wakefulness
Development: Help child recognize emotions, encourage play with other children, start looking for signs of toilet training readiness, limit screen time to 1-2 hr/day, establish a routine and stick to it, clear/consistent limits and a lot of positive praise, read together daily, can start thinking about preschool enrollment around 2.5
Sleep: Maintain consistent bedtime routine, try to introduce a comfort object (blanket, stuffed animal) to help with any nighttime awakenings, if awakening at night, provide quick reassurance and return to bed
Nutrition: Ensure no more than 16-24 oz cow’s milk daily, ensure no more bottle, trust a toddler to know when they are full, try to have family meal times, often have to offer a new food several times
Safety: Rear facing car seat until age 2 or highest weight allowed by manufacturer, childproof home, poison control number (1-800-222-1222), be within arm’s reach near water/pools/bathtubs, discuss gun safety, install stair/window gates now that child is walking/climbing, wear helmets on bikes/scooters, teach street safety
Dental: Brush teeth twice daily
22.11.3.3 Follow up
2.5-3 year CPE, 1st dental visit at 1 year old or w/i 6 months of 1st tooth eruption
22.12 3 Year Old WCC
22.12.1 HPI
22.12.1.1 IN/OUTs
Eat w/ family, 3 meals and 2-3 snacks spaced evenly. 1-2% milk.
Starts developing preferences, important to introduce healthy foods multiple times
Beginning of awareness of urges to urinate and stool, discomfort in diaper, interested in toileting
22.12.1.2 DEVELOPMENT
See chart above
22.12.2 Exam
Full exam
Weight, height: growing along curve
Observe language and socialization
22.12.3 A/P
22.12.3.1 Vaccines/Screenings
Vaccines: MMRV and flu
CBC and lead
Begin BP screening
22.12.3.2 Anticipatory Guidance
When to call: Temperature, decreased feeding, decreased wakefulness
Development: Encourage child to talk about feelings/experiences, encourage age appropriate imaginative/interactive play, continue to read together and allow child to “tell” the story, limit screen time to 1-2 hrs/day
Sleep: Maintain consistent bedtime routine, try to introduce a comfort object (blanket, stuffed animal) to help with any nighttime awakenings, if awakening at night, provide quick reassurance and return to bed
Nutrition: Ensure no more than 16-24 oz cow’s milk daily, trust a toddler to know when they are full, try to have family meal times, often have to offer a new food several times, limit juice
Safety: Forward facing car seat, switch to booster when child is at the highest weight allowed by carseat, teach street safety, discuss gun safety, wear helmets on bikes/scooters, can discuss protective factors of family/child resilience, poison control number (1-800-222-1222), be within arm’s reach near water/pools/bathtubs
Dental: Brush teeth twice daily
22.12.3.3 Follow up
Yearly CPE, yearly dental visit
22.13 4 Year Old WCC
22.13.1 HPI
22.13.1.1 IN/OUTs
Eat w/ family, 3 meals and 2-3 snacks spaced evenly. 1-2% milk.
Starts developing preferences, important to introduce healthy foods multiple times
Should be toilet trained
22.13.1.2 DEVELOPMENT
See chart above
22.13.2 Exam
Full exam
Weight, height: growing along curve
Observe language and socialization
22.13.3 A/P
22.13.3.1 Vaccines/Screenings
Vaccines: DTAP, IPV and flu
CBC and lead
Hearing and vision screening
22.13.3.2 Anticipatory Guidance
When to call: Temperature, decreased feeding, decreased wakefulness
Development: Encourage child to talk about feelings/experiences, make opportunities for daily play, continue to read together and allow child to “tell” the story, limit screen time to 1-2 hrs/day, ask about plans for kindergarten
Sleep: Maintain consistent bedtime routine, try to introduce a comfort object (blanket, stuffed animal) to help with any nighttime awakenings, if awakening at night, provide quick reassurance and return to bed, might eliminate daytime naps
Nutrition: Ensure no more than 16-24 oz cow’s milk daily, try to have family meal times, limit juice
Safety: Forward facing car seat, switch to booster when child is at the highest weight allowed by carseat, teach street safety, discuss gun safety, wear helmets on bikes/scooters, can discuss protective factors of family/child resilience, poison control number (1-800-222-1222), be within arm’s reach near water/pools/bathtubs, discuss rules for safety with adults (no secrets, safe touching)
Dental: Brush teeth twice daily w/ pea-sized amount of toothpaste
22.13.3.3 Follow up
yearly CPE, yearly dental visit
22.14 School Age (~5-10)
22.14.1 HPI
22.14.1.1 IN/OUTs
Emphasize healthy eating and continue to introduce healthy foods even if child does not like. Limit calorie containing beverages.
Typically toilet training; screen for enuresis/encopresis
22.14.1.2 DEVELOPMENT
Assess school readiness (language understanding and fluency, communication of feelings). Provide opportunities for socialization and structured learning experiences like early childhood programs or pre-school.
School readiness includes SDH, think about organizations that could help your family navigate school system, particularly if there are any special needs
22.14.2 Exam
Full exam including back exam for scoliosis
Weight, height: growing along curve
22.14.3 A/P
22.14.3.1 Vaccines/Screenings
9y Vaccines: HPV and flu (second HPV in 6mo or at next WCC visit)
BP screening yearly
Hearing and vision screening at 5y
Obesity screening
Lipid screening once between 9-11
22.14.3.2 Anticipatory Guidance
Discuss 5-2-1-0 rule for nutrition: 5 servings of fruits/veggies, 2 hours or less of screen time daily, 1 hour of physical activity and 0 sugary beverages
Safety: emphasize accident prevention including drowning prevention and water safety/firearm safety, teach child how to be safe with other adults (safe touching, no secrets), always wear a seatbelt, always wear helmets on bikes/scooters, discuss street safety
Address SDH and protective factors of family/child resilience
22.14.3.3 Follow up
Yearly CPE, twice yearly dental visit
22.15 Middle School (~11-13)
22.15.1 HPI
22.15.1.1 IN/OUTs
Emphasize healthy eating and continue to introduce healthy foods even if child does not like. Limit calorie containing beverages. Allow child to choose between healthy options and be involved in food preparation.
22.15.1.2 DEVELOPMENT
Evaluate for school challenges. Discuss bullying, peer group, after school activities.
22.15.2 Exam
Full exam
Weight, height: growing along curve
22.15.3 A/P
22.15.3.1 Vaccines/Screenings
11y Vaccines: TDap#1, MCV#1 and flu
BP screening
Lipid screening once between 9-11
Obesity screening
22.15.3.2 Anticipatory Guidance
Talk to child alone or discuss that this will happen at next visit.
Discuss 5-2-1-0 rule for nutrition: 5 servings of fruits/veggies, 2 hours or less of screen time daily, 1 hour of physical activity and 0 sugary beverages
Discuss puberty and sexuality and gender identity.
Discuss drugs, tobacco products, and alcohol
Discuss mental health, mood, and how to seek help
Firearm and fire safety.
Always wear seatbelt and helmet
Consistent limit setting and encourage positive behaviors
Address SDH and protective factors of family/child resilience
22.15.3.3 Follow up
Yearly CPE, Twice yearly dental visit
22.16 Adolescence (~13-18)
22.16.1 HPI
22.16.1.1 IN/OUTs
Emphasize healthy eating and healthy choices. Discuss what child purchases and chooses for his or herself.
22.16.1.2 DEVELOPMENT
Evaluate for school challenges. Discuss bullying, peer group, after school activities. Discuss college preparation and resources for college assistance.
22.16.2 Exam
Full exam
Weight, height: growing along curve
22.16.3 A/P
22.16.3.1 Vaccines/Screenings
16y Vaccines: MCV#2 and flu
BP screening
Obesity screening
Yearly GC/CT in sexually active females
22.16.3.2 Anticipatory Guidance
Talk to child alone
Discuss 5-2-1-0 rule for nutrition: 5 servings of fruits/veggies, 2 hours or less of screen time daily, 1 hour of physical activity and 0 sugary beverages
Assess satisfaction with current weight and risk factors for eating disorders
Continue to discuss sexuality and gender identity. Discuss safe sexual practices.
Discuss drugs, tobacco products, and alcohol.
Discuss mental health, mood, and how to seek help. Assess for suicide risk.
Firearm safety
Consistent limit setting and encourage positive behaviors
Always wear seatbelt and helmet
Address SDH and protective factors of family/child resilience
22.16.3.3 Follow up
Yearly CPE, Twice yearly dental visit
22.17 Vaccine Schedule (Birth to 18 years)
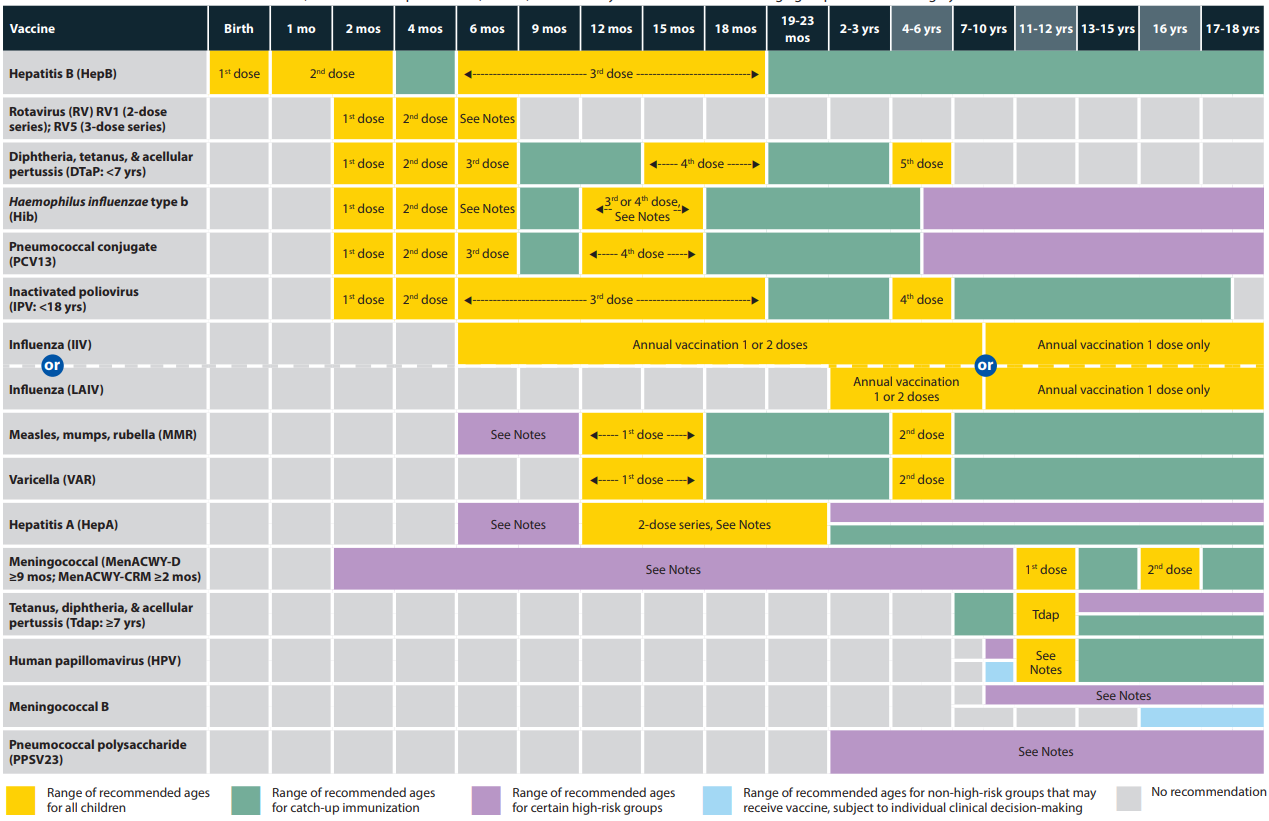
vaccine_schedule_birth_to_18
Recommended Child and Adolescent Immunization Schedule by Medical Indication.
22.18 CHPCC Vaccine Schedule
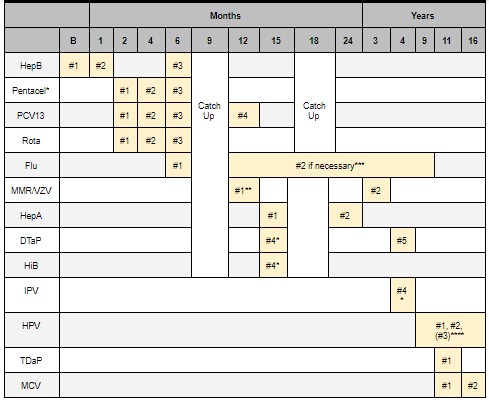
CHPCC vaccine schedule
* PENTACEL = HiB + DTaP + IPV. PEDIARIX = HepB + DTap + IPV. KINRIX = DTaP + IPV
** MMR + VZV (separate) given @ 12m, combined MMRV @ 3 y/o
*** Children 6m - 9y who have never had flu vaccine require 2 doses, 4 weeks apart.
**** If HPV course started before 15th birthday, only need two doses. Each dose should be 6-12m apart.
22.19 CHPCC Screening Schedule
CHPCC screening schedule
22.20 BMC Clinic Screening Questionnaire Schedule
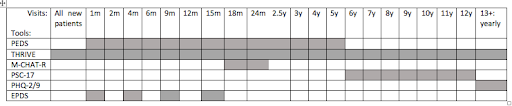
BMC clinic screening
22.21 Autism Management in Primary Care Clinic (**CHOP EBG)
22.21.1 Who to Screen
All children at 18 mo and 24 or 30 mo
Any child over 12 mo with concerns
Risk factors for ASD: sibling w/ ASD, unusual social responses, genetic disorder
22.21.2 How to Screen
PEDS questionnaire @ every visit
Do you have any concerns about your child’s development or behavior?”
MCHAT-R or MCHAT-R/F (modified checklist for autism in toddlers) at 18mo and 24mo
22.21.3 Developmental Red Flags
Diminished, atypical, or no babbling by 12 months
Diminished, atypical, or no gesturing (e.g., pointing, waving bye-bye) by 12 months
Lack of response to name by 12 months
No single words by 16 months
Diminished, atypical, or no two-word spontaneous phrases (excluding echolalia or repetitive speech) by 24 months
Loss of any language or social skill at any age
Lack of joint attention
22.21.4 Positive screening - what now?
Formal audiology testing
Early Intervention (EI) referral (<5 years old), EI services end at 2 years and 9 months
DBP or ASK clinic referral for all
Other specialty referrals as needed
22.21.5 Follow up
1 month after positive screening w/ primary provider for continuity
Ensure EI referral was placed, answer family questions, make sure school is involved for children older than 2.9 years
22.22 ADHD
22.22.1 EBGs
ADHD, adolescents; ADHD, pre-school and school-age
22.22.2 ADHD Definition
Persistent and pervasive inattention, hyperactivity, and/or impulsivity affecting cognitive, academic, behavioral, emotional, and social functioning in more than one setting.
22.22.3 How to Screen
PSC-17, attention score of 7+ should prompt further assessment for ADHD
Age 4+ year: Vanderbilt Assessment Scales (Diagnostic) (print from internet)
To be filled out by parent and teacher
Obtain detailed information from teacher, including report cards, IEP
22.22.4 Common Coexisting Disorders
Learning disabilities
Tic disorders
Anxiety
Depression
OCD
ODD
Substance abuse
22.22.5 Additional Evaluation PRN
PT/OT for motor deficits
Speech/language eval if needed
Labs/imaging if risk factors for alternate organic diagnosis:
- Blood lead levels, TSH, neuroimaging, EEG
22.22.6 Considerations Prior to Initiating Pharmacotherapy
Age: If <6, start with short acting and ensure they are also in behavioral therapy
Make sure to document baseline height, weight, BP, HR and allergies
Make sure to ask about personal hx of substance use, can consider nonstimulant or vyvanse (prodrug, thus lower abuse potential) if hx of SUD
Take a thorough history including personal hx of cardiac disease, epilepsy, tics or comorbid psychiatric conditions and family hx of cardiac disease or sudden cardiac death
- If any concerning cardiac personal or family hx: obtain ekg and consider discussion with cardiology prior to starting stimulant medications
Consider subspecialty consultation if age <6, significant psychiatric comorbidities, cardiac concerns, hx of epilepsy or tourette syndrome
* See medication chart below for more information about common ADHD medications
22.22.7 Follow Up
See patient for dose titration follow up every 1-2 weeks
Up titrate dose until symptom remission, max FDA approved dose or patient experience treatment limiting side effects
If patient is experiencing significant side effects or not having symptom remission can switch drug class (ie methylphenidate to amphetamine)
If patient is well controlled in the AM and experiencing relapse of symptoms in afternoon, can consider adding in afternoon short acting medication
Make sure to document height, weight, BP and HR at each follow up visit
Repeat vanderbilt forms once patient at stable dose of medication
All children with ADHD qualify for a 504
Provide a diagnosis letter to school See patient in clinic every 3-6 months once at stable dose of medication with tolerable side effects
22.22.8 General Prescribing Principles
In children 6 years and older, long-acting formulations are first line (improved compliance, lower abuse potential
In children <6 years, short-acting formulations are first line. In this age group, medication should always be used in conjunction with therapy.
Increase dose until either 1) symptoms are in remission, 2) patient encounters dose-limiting side effects, or 3) maximum daily dose is reached
Before switching medication class 1) maximize dose, 2) optimize dosing schedule, and 3) manage side effects
22.22.9 Stimulants
22.22.9.1 Methylphenidates
First Line
| Drug Name | Starting Dose & Titration | Duration of Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ritalin | Start with 5 mg 1-2 times per day and increase by 5 mg per week until good control achieved. May need additional reduced dose in the afternoon. Max daily dose: 60 mg | 3-4 hrs | Oral solution or chewable tablets |
| Ritalin SR or LA | Start with 20 mg in the morning and increase by 20 mg per week until good control achieved. May need second dose or regular Ritalin dose in the afternoon. Max daily dose: 60 mg | 4-8 hrs | Capsules can be opened and sprinkled. Offers steady release of medication throughout the day |
| Focalin | Start with 2.5 mg per day and increase by 2.5-5 mg per week until good control achieved. Max daily dose: 40 mg | 3-4 hrs | Focalin is twice as potent as other methylphenidates, so halve dose when converting to Focalin |
| Focalin XR | Start with 5 mg per day and increase by 5 mg per week until good control achieved. Max daily dose: 30 mg | 8-12 hrs | Capsules can be opened and sprinkled |
| Concerta | Start at 18 mg each morning and increase by 18 mg each week until good control achieved. Max daily dose: 72 mg | 8-12 hrs | Not ideal for children who cannot swallow pills |
22.22.9.2 Amphetamines
Second Line due to higher incidence of side effects
| Drug Name | Starting Dose & Titration | Duration of Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adderall | Start with 5 mg 1-2 times per day and increase by 5 mg per week until good control achieved. Max daily dose: 40 mg | 4-6 hrs | |
| Adderall XR | Start with 10 mg in the morning and increase by 10 mg per week until good control is achieved. Max daily dose: 40 mg | 8-12 hrs | Capsules can be opened and sprinkled |
| Vyvanse | Start with 30 mg in the morning and increase by 10-20 mg per week until good control achieved. Max daily dose: 70 mg | 10-12 hrs | Capsules can be opened and sprinkled. Low abuse potential. |
Stimulant Side Effects: Anorexia/weight loss, insomnia, irritability, headache, stomachache, increased BP/HR, tics (rare)
22.22.9.3 Non-Stimulants
Third Line
22.22.9.3.1 Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors
| Drug Name | Starting Dose and Titration | Duration of Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atomoxetine (Strattera) | Start with 0.5 mg/kg/day and increase after at least 3 days to target dose of 1.2-1.4 mg/kg/day. Max daily dose: 1.4 mg/kg or 100 mg, whichever is less | FDA approved pediatric depression age 8+, most consistent evidence, long half-life, assoc w behavioral activation | Takes 4-6 weeks to see effects |
NRI side effects: Nausea, GI upset, insomnia, sedation, decreased appetite
22.22.9.3.2 Alpha Agonists
| Drug Name | Starting Dose & Titration | Duration of Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clonidine ER (Kapvay) | Start with 0.1 mg at bedtime and increase by 0.1 mg per week until good control achieved. Max daily dose: 0.4 mg | 12-24 hrs | Helpful for use as sleep aid as well |
| Guanfacine ER (Intuniv) | Start with 1 mg per day and increase by 1 mg per week until good control achieved, target dose 0.05-0.12 mg/kg/day. Max daily dose: 7 mg | 12-24 hrs | First line in Tourette’s |
Alpha agonist side effects: hypotension, sedation, lightheadedness, dry mouth
22.23 Anxiety
22.23.1 Types of Anxiety Disorders
Selective mutism, separation anxiety disorder, phobias, OCD, social anxiety disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder
- Important to screen in patients with ADHD and to screen for ADHD in those with anxiety–often linked
22.23.2 How to Screen
PSC-17 (Pediatric Symptom Checklist): 4+ year olds
Looks at psychosocial functioning, externalization and internalization SDQb (Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire): 3 year olds +
Sensitivity: 63% to 94% for emotional symptoms
Specificity: 88% to 98% conduct problems
Separate scale assesses impact of symptoms on global functioning ASQ-SE (Ages and stages questionnaire—social emotional): 6-60 months
Screens for social-emotional communicative, motor, problem- problems
Sensitivity: 71% to 85%
Specificity: 90% to 98%
22.23.3 Positive Screening
Obtain detailed hx re: symptoms, freq, duration, severity, degree of distress or interference
Consider SW involvement as needed
Behavioral Health/Psych referral
22.23.4 Initial treatment (school aged)
CBT
Fluoxetine 10 mg daily - can uptitrate to 20 mg daily
What if symptoms persist? (school age): SSRI treatment in consult w/ psych, see medication table below for further recommendations
22.24 Depression
22.24.1 Background
Extremely significant cause of morbidity/mortality in children, >⅓ children experience a psychiatric disorder by childhood.
Cormorbidity with ADHD very common, important to screen for both.
Many types but most often will see:
Unipolar major depression (MDD): at least 2 weeks of depression plus 4 neurovegetative symptoms, no hx of mania
Persistent depressive disorder (Dysthmia): depression for >2 years and at least 2 other symptoms (or MDD that persists for 2 years+)
22.24.2 Neurovegetative Symptoms (SIGECAPS)
Sleep disruption
Interest deficit
Guilty Feelings
Energy deficit
Concentration deficit
Appetite disorder
Psychomotor Changes
Suicidality
22.24.3 How to Screen
Always screen for history of mania or bipolar symptoms (25-30% of Bipolar Disorder starts with depressive episode)
Use PSC internalizing scale for anxiety/depression
PHQ-9
* Important to consider referral to psychiatrist for severe symptoms, significant comorbidities and for children <12
22.24.4 Therapy
Should always be concurrent with starting medications (or offered), particularly in younger children. See tables below re medication management
22.24.5 Follow Up
Follow up 2 wks after initiation and then 2-4 wks after, monitoring closely.
Most symptom improvement in 6-8 wks with some mild effects seen at 2 wks.
22.25 Medication Management: Anxiety and Depression
22.25.1 Side Effects/Precautions with SSRI use (see chart below for medication recs)
Black box warning:
Increase in suicidality/self harm after dose initiation or increase in dose
Important to monitor closely during any initiation or changes
Often suicidality exists prior to starting medication and important to assess prior and during medication management
SSRI Activation Syndrome/Induced Mania
Irritability, restlessness, agitation, impulsivity, hyperactivity, manic symptoms, psychosis
Often emerges with initiation of SSRI or dose increase
Risk higher in younger children and those at risk for bipolar disorder
QTc prolongation/cardiac events seen in escitalopram and citalopram in particular, consider closer monitoring or avoiding in patients with cardiac history
Avoid Wellbutrin in patients with eating disorders or seizure history
- Important to do good diet history prior to initiation given common disordered eating, particularly in adolescents
Serotonin syndrome
Most common mild side effects: GI, HA, sleep disturbances
22.25.2 Anxiety
| SSRI | Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Sertraline (Zoloft) | 50-200 mg | FDA approved pediatric OCD age 6+ (POTS), often requires high doses for OCD |
| Fluvoxamine (Luvox) | 100-300 mg | FDA approved pediatric OCD ages 8+, BID dosing, monitor for drug/drug interactions |
| Fluoxetine (Prozac) | 20-40 mg | FDA approved pediatrics OCD 7+, long half-life, behavioral activation |
| Escitalopram (Lexapro) | 20-40 mg | FDA-approved pediatric depression, dose related QTc prolongation; lower side effect profile |
| Citalopram (Celexa) | 20-40 mg *Do not exceed 40 mg daily given QTc prolongation | Dose related QTc prolonging; lower side effect profile |
22.25.3 Depression
First line: SSRI
| SSRI | Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Fluoxetine (Prozac) | 20-40 mg | FDA approved pediatric depression age 8+, most consistent evidence, long half-life, assoc w behavioral activation |
| Escitalopram (Lexapro) | 20-40 mg | FDA approved for adolescent depression 12+, well tolerated |
| Sertraline (Zoloft) | 5-200 mg | FDA approved pediatrics OCD 7+ |
| Citalopram (Celexa) | 20-40 mg | QTc prolongation concern but lower side effects otherwise; do not exceed 40 mg daily |
Second line: another SSRI
Try increasing dose of first before switching to a second
Switch to second SSRI if one is not working or side effects bothersome with first attempt
Third line: Refer to specialist; medications include venlafaxine, bupropion, mirtazapine, duloxetine
- Should be done in conjunction with a specialist
22.26 BMC Primary Care Clinic Resources
22.26.1 Asthma Education
WHAT: 5-10 minute check in w/ patients to review triggers, spacer teaching, med teaching, Asthma Action Plan,, screening for in home asthma services such as Breathe Easy
WHEN: Monday-Friday 9am-5pm. Appropriate for any patient w/ asthma here for WCE, urgent visit, etc.
HOW: Reachable via pager 8818p
22.26.2 Reach out and Read (ROR)
WHAT: Program to promote early literacy
WHO: Age child 6 months – 5 years
HOW: Kids ages 6 months – 5 years receive a book at every well child visit.
WHERE: The ROR books are located in the little office next to the nursing office in the main primary care clinic hallway – they are next to a bunch of stickers too!!
22.26.3 Lactation Resources
WHAT: We have lactation consults (both in the clinic and in the newborn nursery) who can often help mom’s during the newborn visits.
WHO: Any mom who is breastfeeding or attempting to breastfeed, especially those who have babies who aren’t gaining good weight. Also appropriate to call them if moms have questions about pumping, latch, nipple pain, etc.
WHEN: Anytime during PC clinic
HOW: You can page the Child Life Specialist who is usually in clinic and can come work w/ moms! You can also page a lactation consultant from the newborn nursery but it is very likely that they will be too busy to come during your visit.
22.26.4 Food Pantry
WHAT: Provides food resources (including fresh fruits and vegetables) to patients w/ food insecurity, chronic illness, etc.
WHO: Anyone who gets a referral; immigration status DOES NOT matter and you don’t need to document income when you refer, you just need to place the referral
WHEN: Open Monday – Friday; 10:00 AM – 4:00 PM; pts can go 2x monthly
HOW: Write a prescription for your patient in EPIC (they MUST have a Rx)
22.26.5 Street Cred
WHAT: Organization started by BCRP alum Lucy Marcil to help families get the maximum amount on their tax returns
WHO: For all pts w/ income <54,000
HOW: Refer patients to street cred (use .STREETCRED in the EMR) info@mystreetcred.org (617) 414-5946
22.26.6 Child Witness to Violence Project
WHAT: Provides social support and counseling for young (< 8y) children who have witnessed domestic violence. Run under the auspices of the DBP clinic.
WHERE: Counseling happens at BMC but there is no documentation left in the chart. This can be tricky because you will not know if your patients are receiving services based on chart review alone.
HOW: Call (617) 414-7425
22.27 BMC Pediatrics Specialty Outpatient Clinics
22.27.1 CCP Clinic
WHAT: Primary care home for patients w/ complex medical problems including NICU grads, patients w/ complex genetic disorders, etc.
WHO: All patients w/ multiple medical problems and/or exceptionally complex social situations AND their siblings
HOW: Talk to Dr. Jack Maypole (BCRP alum!)
22.27.2 GROW Clinic
WHAT: BMC based clinic for kids w/ FTT, provides comprehensive wrap around services including social work and home visits performed by a dietician. Not a PCP
WHO: For FTT kiddos (I think only less than age 5)
HOW: Talk to the Grow clinic patient navigator (refer in EPIC)
22.27.3 Baby Steps Clinic
WHAT: Provides coordination of care for babies who are preterm or have had complicated newborn courses; NOT primary care. Comprehensive team including pediatrician, nutritionist, OT, dieticians and close communication w/ neuro and GI
WHO: For any baby who had a tough newborn course, is having difficulty gaining weight or other challenges. (All preterm)
HOW: This is usually done when the baby leaves the nursery but if you think a baby would benefit from this clinic as well you can place a referral in EPIC
22.28 SoFAR Clinic
WHAT: Primary Care Clinic for moms w/ a history of substance use and their babies (babies w/ a history of NAS) or exposure
WHO: Babies born to moms who struggled w/ substance use during pregnancy and their siblings. Moms get care too–Dyadic approach!
HOW: Usually referred to the clinic from the newborn nursery but this can also be done on the outpatient side. Reach out to SoFar clinic SW to schedule an intake for the family.
22.28.1 Teen and Tot Clinic
WHAT: Primary Care Clinic for teen moms and their babies – teen girls can get prenatal care in a centering group by midwife. Teen girls and children are seen together during primary care visits. The clinic also has a patient navigators and is run by Dr. Pierre-Joseph
WHO: Teen moms and their babies/pregnant teens who have elected to become parents
HOW: Page Adrian Stevenson (teen and tot patient navigator) or talk to Dr. Adolphe or Dr. Pierre-Joseph to transfer maternal/newborn care to teen and tot. Adrian will talk to the mom and do an intake
22.28.2 IEP Clinic
WHAT: Clinic that is run by BMC preceptor Dr. Adolphe that bridges primary care w/ DBP, Helps w/ ADHD, ASD, learning/intellectual disorders. Appropriate for kids w/ IEP who aren’t making progress or accessing the curriculum well or if parents have questions about the IEP.
WHEN: Usually takes patients ~ 1 month to get in (for now)… if you need help sooner or in the meantime, reach out to Dr. Adolphe directly.
HOW: Place a referral in EPIC
22.28.3 Family Planning Services
Birth control counseling, STD testing, options counseling, for patients of ANY AGE, same-day birth control available page Teakia Brown
22.28.4 Pain Clinic
For kids with chronic pain (including functional), MD, acupuncturist, psychologist, PT
22.28.5 CATALYST Clinic
Teens with substance use disorder
22.28.6 Menstrual Disorders Clinic
Joint Adolescent/Heme Clinic
22.28.7 Lead Clinic
Sean Palfrey, for kids with elevated lead
22.28.8 CATCH Clinic
For gender affirming care
22.28.9 Embedded Child Psychiatrist
Andrea Spencer available for “curbside consults” and “co-management of patients with behavioral health concerns”– page directly or refer to Integrated Behavioral health
22.30 BMC Clinic Tips
Always review medications, allergies, etc by going to the A/P section of epic and clicking “mark all as reviewed”
You can delete a note by clicking the “X” by the “sign note” or “pend note” drop down
When ordering immunizations, use the order sets, which are present under “A/P” order section
- Simply check off the box and sign the orders
Huddle w/ your nurse and CA prior to clinic to discuss patients that may be late, clinic flow goals, complex patients, anticipated orders
You know a patient is roomed when their vitals populate into your note
To promote continuity, staple your card to the after visit summary
You must import the flowsheets for the developmental screens into your note & indicate positive or negative
You must send your notes to your preceptor w/i 48 hours for signing and billing
22.31 CHPCC Co-Located “Specialty” Clinics
Refer patients with a PowerChart Order
22.31.1 Asthma Clinic
In-depth education or intervisit care, including home visits, for asthma patients requiring more frequent visits and/or asthma patients with more severe disease.
22.31.2 Advocating Success for Kids (ASK)
A multidisciplinary team (developmental medicine, educational specialist, social worker, and primary care) assists children who are having academic difficulties, such as from ADHD or a learning disability, who are not making adequate progress despite having an IEP, and also conducts evaluations for autism spectrum disorder and other developmental delays.
22.31.3 Rainbow
A multidisciplinary team to coordinate care for our clinic’s medically complex children. Owing to their medical complexity, patients with a “Rainbow” distinction get longer patient visits, inter-visit monitoring, and additional nursing, social work, and case management support.
22.31.4 RASH
Have your patients’ skin concerns addressed quickly, in a primary care setting, by pediatricians. This is generally far faster than a referral to dermatology.
22.31.5 Young Parents Program (YPP)
A teen-tot clinic that provides primary care for adolescent parents and their children. Dedicated YPP staff provide longitudinal supports.
22.32 CHPCC Contacts
Fax: 617-730-0505
Charge RN: 84706
Front Desk: 58944
SW Pager: 0170
Child Life: 84708
Dental Clinic: 5654
Lactation: 56445
Newborn Pager (for scheduling visits): 5222
Navigator: 5931
YPP: 7718
22.3.1.5 SOCIAL
Who lives at home, who is involved w/ care
Screen for postpartum depression/baby blues
Assess mood of primary caretaker, can be exhausting and difficult time